Natural language names
 | Textstil - Schriftensatz - Modell |
 | Text Style Font Model |
 | Modèle de police de style de texte |
Change log
| Item | SPF | XML | Change | Description | IFC2x3 to IFC4 4.0.0.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IfcTextStyleFontModel | MOVED | Schema changed from IFCPRESENTATIONRESOURCE to IFCPRESENTATIONAPPEARANCERESOURCE. | ||
| FontFamily | MODIFIED | Instantiation changed from OPTIONAL. | IFC2x3 to IFC4 4.0.0.0 | |
| IfcTextStyleFontModel | MOVED | Schema changed from IFCPRESENTATIONRESOURCE to IFCPRESENTATIONAPPEARANCERESOURCE. | ||
| FontFamily | MODIFIED | Instantiation changed from OPTIONAL. |
Semantic definitions at the entity
Entity definition
Definition according to W3C for Cascading Style Sheets:
Setting font properties will be among the most common uses of style sheets. Unfortunately, there exists no well-defined and universally accepted taxonomy for classifying fonts, and terms that apply to one font family may not be appropriate for others. For example, 'italic' is commonly used to label slanted text, but slanted text may also be labeled as being Oblique, Slanted, Incline, Cursive or Kursiv. Therefore it is not a simple problem to map typical font selection properties to a specific font.
Font matching
Because there is no accepted, universal taxonomy of font properties, matching of properties to font faces must be done carefully. The properties are matched in a well-defined order to ensure that the results of this matching process are as consistent as possible across user agents (assuming that the same library of font faces is presented to each of them).
- The user agent makes (or accesses) a database of relevant CSS1 properties of all the fonts of which the UA is aware. The UA may be aware of a font because it has been installed locally or it has been previously downloaded over the web. If there are two fonts with exactly the same properties, one of them is ignored.
- At a given element and for each character in that element, the UA assembles the font-properties applicable to that element. Using the complete set of properties, the UA uses the 'font-family' property to choose a tentative font family. The remaining properties are tested against the family according to the matching criteria described with each property. If there are matches for all the remaining properties, then that is the matching font face for the given element.
- If there is no matching font face within the 'font-family' being processed by step 2, and if there is a next alternative 'font-family' in the font set, then repeat step 2 with the next alternative 'font-family'.
- If there is a matching font face, but it doesn't contain a glyph for the current character, and if there is a next alternative 'font-family' in the font sets, then repeat step 2 with the next alternative 'font-family'.
- If there is no font within the family selected in 2, then use a UA-dependent default 'font-family' and repeat step 2, using the best match that can be obtained within the default font.
(The above algorithm can be optimized to avoid having to revisit the CSS1 properties for each character.)
The per-property matching rules from (2) above are as follows:
- 'font-style' is tried first. 'italic' will be satisfied if there is either a face in the UA's font database labeled with the CSS keyword 'italic' (preferred) or 'oblique'. Otherwise the values must be matched exactly or font-style will fail.
- 'font-variant' is tried next. 'normal' matches a font not labeled as 'small-caps'; 'small-caps' matches (1) a font labeled as 'small-caps', (2) a font in which the small caps are synthesized, or (3) a font where all lowercase letters are replaced by upper case letters. A small-caps font may be synthesized by electronically scaling uppercase letters from a normal font.
- 'font-weight' is matched next, it will never fail. (See 'font-weight' below.)
- 'font-size' must be matched within a UA-dependent margin of tolerance. (Typically, sizes for scalable fonts are rounded to the nearest whole pixel, while the tolerance for bitmapped fonts could be as large as 20%.) Further computations, are based on the 'font-size' value that is used, not the one that is specified.
The inherited Name attribute is used to define the font name, particularly in cases, where no (list of) font families are provided.
NOTE Corresponding CSS1 definitions are Font properties ('font-family', 'font-style', 'font-variant', 'font-weight').
HISTORY New entity in IFC2x3.
Attribute definitions
| # | Attribute | Type | Cardinality | Description | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | FontFamily | IfcTextFontName | L[1:?] |
The value is a prioritized list of font family names and/or generic family names. The first list entry has the highest priority, if this font fails, the next list item shall be used. The last list item should (if possible) be a generic family.
IFC4 CHANGE Attribute changed to being mandatory. | X |
| 3 | FontStyle | IfcFontStyle | ? | The font style property selects between normal (sometimes referred to as "roman" or "upright"), italic and oblique faces within a font family. | X |
| 4 | FontVariant | IfcFontVariant | ? |
The font variant property selects between normal and small-caps.
NOTE It has been introduced for later compliance to full CSS1 support. | X |
| 5 | FontWeight | IfcFontWeight | ? |
The font weight property selects the weight of the font.
NOTE Values other then 'normal' and 'bold' have been introduced for later compliance to full CSS1 support. | X |
| 6 | FontSize | IfcSizeSelect |
The font size provides the size or height of the text font.
NOTE The following values are allowed, <IfcLengthMeasure, with positive values, the length unit is globally defined at IfcUnitAssignment.__ | X |
Formal Propositions
| Rule | Description |
|---|---|
| MeasureOfFontSize | The size should be given by a positive length measure, |
Inherited definitions from supertypes
Entity inheritance
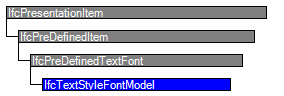
Attribute inheritance
| # | Attribute | Type | Cardinality | Description | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IfcPresentationItem | |||||
| IfcPreDefinedItem | |||||
| 1 | Name | IfcLabel | The string by which the pre defined item is identified. Allowable values for the string are declared at the level of subtypes. | X | |
| IfcPreDefinedTextFont | |||||
| IfcTextStyleFontModel | |||||
| 2 | FontFamily | IfcTextFontName | L[1:?] |
The value is a prioritized list of font family names and/or generic family names. The first list entry has the highest priority, if this font fails, the next list item shall be used. The last list item should (if possible) be a generic family.
IFC4 CHANGE Attribute changed to being mandatory. | X |
| 3 | FontStyle | IfcFontStyle | ? | The font style property selects between normal (sometimes referred to as "roman" or "upright"), italic and oblique faces within a font family. | X |
| 4 | FontVariant | IfcFontVariant | ? |
The font variant property selects between normal and small-caps.
NOTE It has been introduced for later compliance to full CSS1 support. | X |
| 5 | FontWeight | IfcFontWeight | ? |
The font weight property selects the weight of the font.
NOTE Values other then 'normal' and 'bold' have been introduced for later compliance to full CSS1 support. | X |
| 6 | FontSize | IfcSizeSelect |
The font size provides the size or height of the text font.
NOTE The following values are allowed, <IfcLengthMeasure, with positive values, the length unit is globally defined at IfcUnitAssignment.__ | X | |
Formal representations
XML Specification
<xs:element name="IfcTextStyleFontModel" type="ifc:IfcTextStyleFontModel" substitutionGroup="ifc:IfcPreDefinedTextFont" nillable="true"/>
<xs:complexType name="IfcTextStyleFontModel">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ifc:IfcPreDefinedTextFont">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="FontFamily">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element ref="ifc:IfcTextFontName-wrapper" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute ref="ifc:itemType" fixed="ifc:IfcTextFontName-wrapper"/>
<xs:attribute ref="ifc:cType" fixed="list"/>
<xs:attribute ref="ifc:arraySize" use="optional"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
<xs:element name="FontSize">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:group ref="ifc:IfcSizeSelect"/>
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:sequence>
<xs:attribute name="FontStyle" type="ifc:IfcFontStyle" use="optional"/>
<xs:attribute name="FontVariant" type="ifc:IfcFontVariant" use="optional"/>
<xs:attribute name="FontWeight" type="ifc:IfcFontWeight" use="optional"/>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
EXPRESS Specification
ENTITY IfcTextStyleFontModel
SUBTYPE OF (IfcPreDefinedTextFont);
FontFamily : LIST [1:?] OF IfcTextFontName;
FontStyle : OPTIONAL IfcFontStyle;
FontVariant : OPTIONAL IfcFontVariant;
FontWeight : OPTIONAL IfcFontWeight;
FontSize : IfcSizeSelect;
WHERE
MeasureOfFontSize : ('IFCMEASURERESOURCE.IfcLengthMeasure' IN TYPEOF(SELF.FontSize)) AND
(SELF.FontSize > 0.);
END_ENTITY;
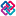
 EXPRESS-G diagram
EXPRESS-G diagram Link to this page
Link to this page