Natural language names
 | (Rechen-)Operation zwischen Koordinatensystemen |
 | Coordinate Operation |
 | Opération entre systèmes de coordonnées de référence |
Change log
| Item | SPF | XML | Change | Description | IFC2x3 to IFC4 4.0.0.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IfcCoordinateOperation | ADDED | IFC2x3 to IFC4 4.0.0.0 | ||
| IfcCoordinateOperation | ADDED |
Semantic definitions at the entity
Entity definition
The coordinate operation is an abstract supertype to handle any operation (transformation or conversion) between two coordinate reference systems. It is meant to provide expandability for future versions, since currently only the conversion of a local engineering coordinate system into a map coordinate reference system is dealt with by the subtype IfcMapConversion.
By convention, a coordinate operation is given between the SourceCRS being the more local, or child coordinate reference system, and the TargetCRS being the more remote or parent coordinate reference system, in the special case the coordinate operation between the local engineering coordinate system of the construction project and any map or other coordinate reference system.
NOTE Definition from OpenGIS Abstract Specification, Topic 2:
If the relationship between any two coordinate reference systems is known, coordinates can be transformed or converted to another coordinate reference system. Coordinate operations are divided into two subtypes:
- Coordinate conversion – mathematical operation on coordinates that does not include any change of datum. The best-known example of a coordinate conversion is a map projection. The parameters describing coordinate conversions are defined rather than empirically derived. Note that some conversions have no parameters.
- Coordinate transformation – mathematical operation on coordinates that usually includes a change of datum. The parameters of a coordinate transformation are empirically derived from data containing the coordinates of a series of points in both coordinate reference systems. This computational process is usually ‘over-determined’, allowing derivation of error (or accuracy) estimates for the transformation. Also, the stochastic nature of the parameters may result in multiple (different) versions of the same coordinate transformation. Because of this several transformations may exist for a given pair of coordinate reference systems, differing in their transformation method, parameter values and accuracy characteristics.
HISTORY New entity in IFC4.
Attribute definitions
| # | Attribute | Type | Cardinality | Description | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SourceCRS | IfcCoordinateReferenceSystemSelect | Source coordinate reference system for the operation. | X | |
| 2 | TargetCRS | IfcCoordinateReferenceSystem | Target coordinate reference system for the operation. | X |
Inherited definitions from supertypes
Entity inheritance
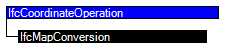
Attribute inheritance
| # | Attribute | Type | Cardinality | Description | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IfcCoordinateOperation | |||||
| 1 | SourceCRS | IfcCoordinateReferenceSystemSelect | Source coordinate reference system for the operation. | X | |
| 2 | TargetCRS | IfcCoordinateReferenceSystem | Target coordinate reference system for the operation. | X | |
Formal representations
XML Specification
<xs:element name="IfcCoordinateOperation" type="ifc:IfcCoordinateOperation" abstract="true" substitutionGroup="ifc:Entity" nillable="true"/>
<xs:complexType name="IfcCoordinateOperation" abstract="true">
<xs:complexContent>
<xs:extension base="ifc:Entity">
<xs:sequence>
<xs:element name="TargetCRS" type="ifc:IfcCoordinateReferenceSystem" nillable="true"/>
</xs:sequence>
</xs:extension>
</xs:complexContent>
</xs:complexType>
EXPRESS Specification
ENTITY IfcCoordinateOperation
ABSTRACT SUPERTYPE OF(IfcMapConversion);
SourceCRS : IfcCoordinateReferenceSystemSelect;
TargetCRS : IfcCoordinateReferenceSystem;
END_ENTITY;
 References: IfcCoordinateReferenceSystem
IfcGeometricRepresentationContext
References: IfcCoordinateReferenceSystem
IfcGeometricRepresentationContext
 EXPRESS-G diagram
EXPRESS-G diagram Link to this page
Link to this page